Describe the Process of Muscle Contraction
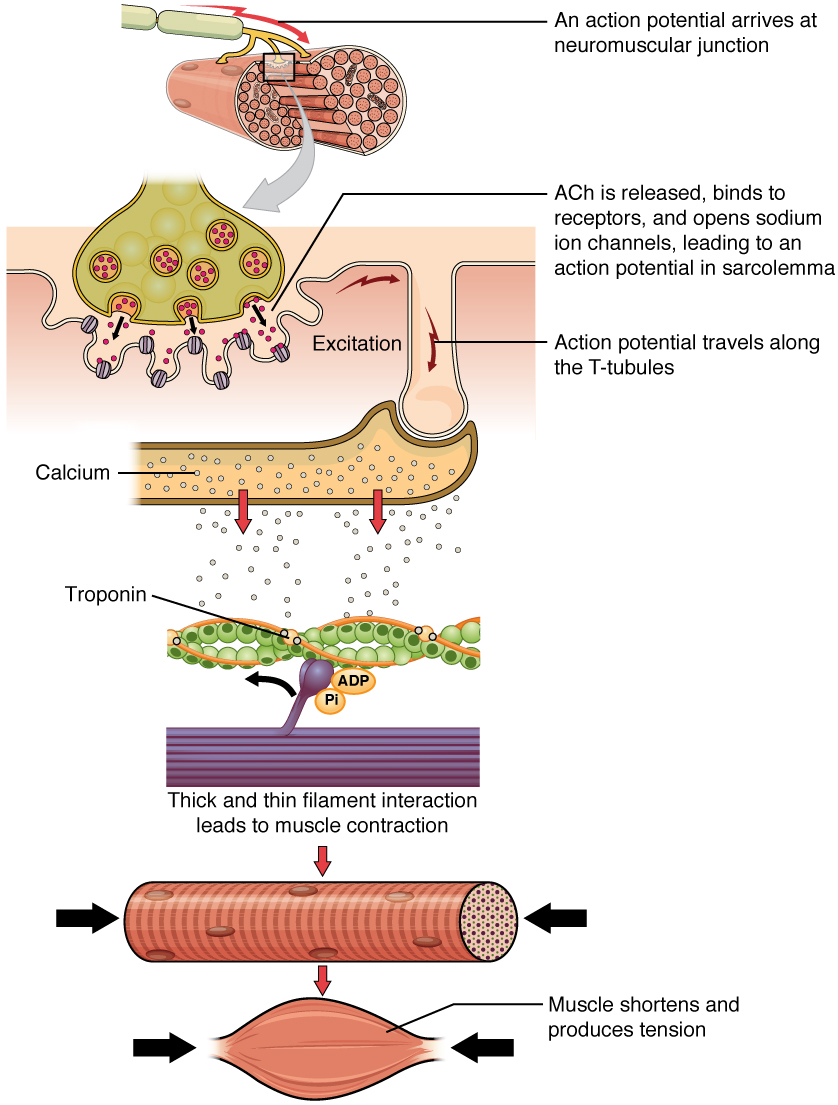
A signal sent by the central nervous system via motor neuron initiates muscle contraction. Skeletal muscle contraction begins first at the neuromuscular junction which is the synapse between a motoneuron and a muscle fiber.

6 4 Muscle Contraction Medicine Libretexts
The neuromuscular junction is a junction between a neuron and the sarcolemma of the muscle fibre.

. Brain sends an impulse. Muscle contraction is initiated by signals that travel along the axon and reach the neuromuscular junction or motor end plate. Sliding Filament Theory of Muscle Contraction.
Current biochemical studies suggest that the myosin cross-bridge exists in two main conformations. Steps to Muscle Contraction. This process is known as the sliding filament model of muscle contraction Figure 6.
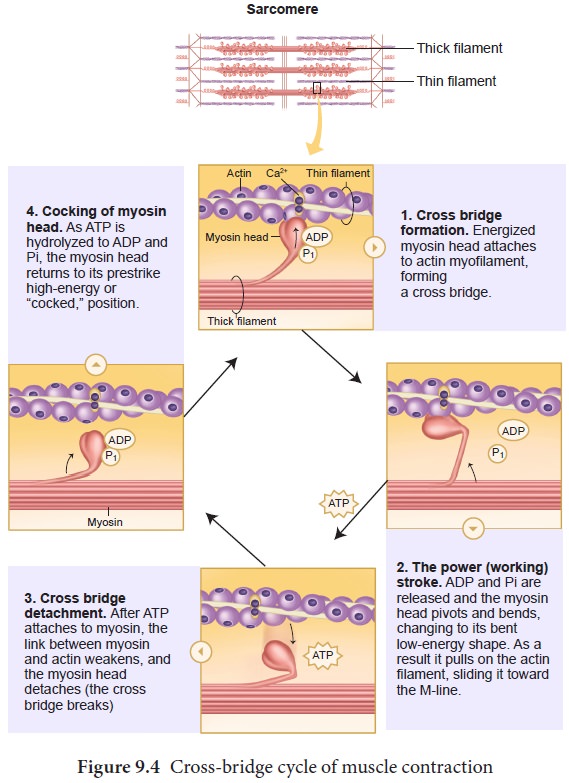
The process of muscle contraction. To initiate muscle contraction tropomyosin has to expose the myosin-binding site on an actin filament to allow cross-bridge formation between the actin and myosin microfilaments. The following list presents an overview of the sequence of events involved in the contraction cycle.
During contraction the thin filaments slide over the thick filaments. The neuromuscular junction is the junction between a motor neuron and sarcolemma. Impulse arrives causing calcium channels to open and enter.
Terms in this set 15 Step 1. Muscle contraction is initiated by signals that travel along the axon and reach the neuromuscular junction or motor end plate. To initiate muscle contraction tropomyosin has to expose the myosin-binding site on an actin filament to allow cross-bridge formation between the actin and myosin microfilaments.
Ach is released from the axon to receptors located on the sarcolemma. Muscle contraction occurs when the thin actin and thick myosin filaments slide past each other. Skeletal muscle cell contraction occurs after a release of calcium ions from internal stores which is initiated by a neural signal.
Isotonic eccentric contraction this involves the muscle lengthening whilst it. Impulse arrives at the synaptic knob. Learn anatomy faster and.
The calcium ions bind to the troponin which reveals the active site on actin by removing tropomyosin. Calcium causes synaptic vesicles to fuse with the membrane. Ad Over 27000 video lessons and other resources youre guaranteed to find what you need.
It is generally assumed that this process is driven by cross-bridges which extend from the myosin filaments and cyclically interact with the actin filaments as ATP is hydrolysed. The first step in the process of contraction is for Ca to bind to troponin so that tropomyosin can slide away from the binding sites on the actin strands. Muscle contraction is initiated by signals that travel along the axon and reach the neuromuscular junction or motor end plate.
Propagation of action potentials to the motoneuron and subsequent depolarization results in the opening of voltage-gated calcium Ca2 channels of the presynaptic membrane. In physiology muscle contraction does not necessarily mean muscle shortening because muscle tension can be produced without changes in muscle length such as when holding something heavy in the same position. The skeletal muscle contraction cycle is activated by calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
The first step in the process of contraction is for Ca to bind to troponin so that tropomyosin can slide away from the binding sites on the actin strands. The Ca2 ions bind to troponin proteins embedded along the thin filaments and the contraction process begins. Muscle Contraction Steps in Detail AcH binds to the AcH receptors present in the sarcolemma increasing its permeability Na enter the sarcolemma changing its polarity and creating an action potential Ca are released by the sarcoplasmic reticulum as the.
Muscle contraction is described by the sliding filament model of contraction. A nerve impulse travels to the. The termination of muscle contraction is followed by muscle relaxation which.
On a muscle cell. Ca2 binds to troponin shifting the actin filaments which exposes binding sites. An action potential in a motor neuron causes acetylcholine to release in the synaptic cleft.
This allows the myosin heads to bind to these. This whole process occurs in a sequential manner. Muscle contraction entails the sliding of the thin filaments past the thick filaments resulting in shortening of the sarcomere and thus the entire myocyte.
The resulting longitudinal force is transmitted through the extracellular matrix ECM to the bone via the tendon. Myosin cross bridges attach detach pulling actin filaments toward center requires ATP Step 4. The binding Ach causes.
Calcium floods into the muscle cell binding with troponin allowing actin and myosin to bind. The sequence of events that result in the contraction of an individual muscle fiber begins with a signalthe neurotransmitter AChfrom the motor neuron innervating that fiber. Action potential generated which stimulates muscle.
The sequence of events involved in a muscle contraction. During skeletal muscle contraction the thick filament slides over the thin filament by a repeated binding and releases myosin along the filament. Acetylcholine binds with receptors on the cell membrane on the muscle fiber opening Ca2 -Na channels.
This whole process occurs in a sequential manner. The sliding filament theory is the most widely accepted explanation for how this occurs. Each skeletal muscle fiber is controlled by a motor neuron which conducts signals from the brain or spinal cord to the muscle.
So lets do a quick review of muscle contraction physiology. The motor nerve stimulates an action potential impulse to pass down a neuron to the. Once the muscle fiber is stimulated by the motor neuron actin and myosin protein filaments within the skeletal muscle fiber slide past each other to produce a contraction.
Is the point where the axons of the nerve meet with the muscle cell. As a result acetylcholine a neurotransmitter is released. Muscle contraction is the activation of tension-generating sites within muscle cells.
As the action potentials travel down the T tubules calcium channels in the nearby terminal cisternae of SR open and Ca2 ions diffuse into the surrounding sarcoplasm. According to this theory muscle contraction. ACh is the neurotransmitter that binds at the neuromuscular junction NMJ to trigger depolarization and an action potential travels along the sarcolemma to trigger calcium release from SR.
During skeletal muscle contraction the thick filament slides over the thin filament by a repeated binding and releases of myosin head along the filament. This whole process occurs in a sequential manner. The origin and insertion of the muscle move closer together and the muscle becomes fatter.
The neuromuscular junction is a junction between.
Mechanism Of Muscle Contraction

Muscle Fiber Contraction And Relaxation Anatomy And Physiology

Comments
Post a Comment